Pre-clinical evaluations of a novel, prompt gamma-ray and fast neutron-based treatment verification system
- Planned secondments: Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (Germany), University of Navarra (Spain) and Cosylab (Slovenia)
- PhD program: Western Norway University of Applied Sciences
Project description
It is now a well-known fact that proton therapy (PT) suffers from range uncertainties that limit the full exploitation of the dosimetric advantages of PT as an effective cancer treatment modality. Range uncertainties might result from errors in the estimation of the proton stopping power in tissue, patient setup errors, anatomical changes and organ motion. To mitigate the undesired effects of range uncertainties, several online range and dose monitoring techniques are being investigated. The project at hand focuses on further developments of a novel concept being developed within the so-called NOVO (Next Generation Imaging for Real-Time Dose Verification Enabling Adaptive Proton Therapy) project.
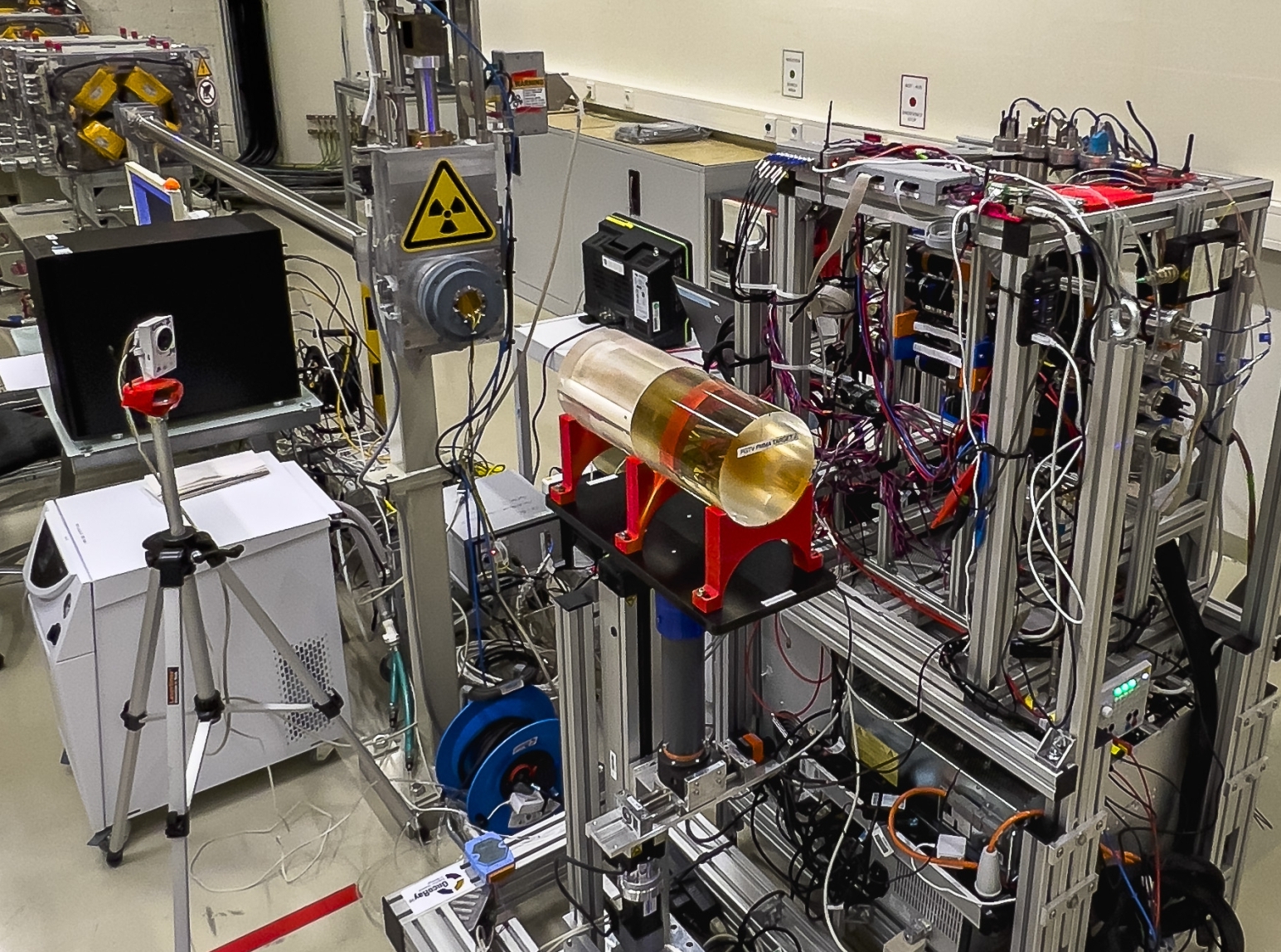
In the NOVO project, a novel detector array, NOVCoDA (the NOVO Compact Detector Array) capable of simultaneous detection and imaging of secondary prompt gamma-rays and fast neutrons is being developed in an international effort funded by the EIC Pathfinder Open. In this project, within RAPTORplus, the candidate will further explore pre-clinical evaluations of NOVCoDA via in-silico models supplied with experimental data collected in clinically relevant proton beamlines. As part of these evaluations, the project will also explore use of advanced data analysis techniques based on Artificial Intelligence (e.g., deep learning techniques and multivariate regressions) to enhance the detection probability of range and dose deviations from the available detector data.
The main objective of the project is the confirmation of range shift detection capabilities of NOVCoDA under pre-clinical conditions as well as unravelling NOVCoDA’s limitations in this regard. As an important part of the project, the clinical translation potential of NOVCoDA will be explored by comparison to the state-of-the-art systems that are based on the detection of secondary prompt gamma-rays, in particular, prompt gamma-ray imaging (PGI) and timing (PGT) systems.
Furthermore, through explorations of the capabilities of NOVCoDA as well as comparisons to PGI and PGT systems, the project will strengthen the ties between RAPTORplus and NOVO consortia.
The candidate hired in this project will be enrolled in the PhD program in Computer Science: Software Engineering, Sensor Networks and Engineering Computing at the Western Norway University of Applied Sciences, Faculty of Technology, Environmental and Social Sciences. During the execution of the project, the candidate will have the opportunity to collaborate with the NOVO team at HVL with access to HVL’s radiation detection laboratory and the HVL high performance computing cluster. As part of the project, the candidate is also expected to have a long secondment at Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf (Germany) where the current prototype of NOVCoDA is located.
For more information concerning the research project please contact:
Ilker Meric

Candidate profile
Doctoral Candidate at Western Norway University of Applied Sciences
- MSc in physics or engineering, ideally with a background in medical physics, radiation physics and/or nuclear engineering.
- Good understanding of radiation detection physics, especially pertaining to indirectly ionizing radiation (gamma-ray and neutron) interactions in organic scintillators.
- Some experience in preparing and running nuclear physics experiments.
- Familiarity with analyzing complex experimental and Monte Carlo simulated data to optimize the analysis of raw detector data in preparation for imaging.
- Proficiency in Monte Carlo simulations (MCNP, Geant4, FLUKA or PHITS) and programming languages (C/C++, Python and/or Fortran).
- Legally able to visit nuclear technology facilities and laboratories, participate in experiments involving radiation detection measurements (especially neutron detection).
- Fluency in English, both written and spoken.
Desired qualifications (can be waived) are:
- Knowledge of proton therapy in general, and range verification techniques based on prompt gamma-ray and neutron imaging and detection.
- Familiarity with image reconstruction methods with particular emphasis on those methods used for nuclear and medical imaging.
- Understanding of data processing pipelines in nuclear physics experiments, including conversion of raw data from detectors in preparation for particle imaging.
- Experience in conducting research in a multidisciplinary environment.
The candidate will receive a salary in accordance with the State Salary Scale, l.pl 17.515, code 1017, NOK 570,000 gross per year. From the salary, 2% is deducted as a contribution to the Norwegian Public Service Pension Fund.

Høgskulen på Vestlandet
PROJECT BENEFICIARY
Western Norway University of Applied Sciences (HVL) is a higher educational institution located along the western coast of Norway which also is one of the largest ones in the country with approximately 16 500 students and 1900 employees. HVL’s five campuses are in Bergen, Førde, Haugesund, Sogndal and on the island of Stord. The RAPTORplus doctoral candidate will be located at the campus in Bergen. Within proton therapy, HVL has a strong track record of hosting externally funded projects related to range and dose monitoring, and strong collaboration with both national and international proton therapy research environments.